Firewall
 Firewall Firewall
|
|
About Firewall
Firewall provides traditional firewall functionality, blocking and/or flagging traffic based on rules.
The term "Firewall" has grown to encompass many functionalities and has a wide array of meanings. The "firewall" is often use interchangeably with "router" "gateway" and "UTM" or "Unified Threat Management" Even the NG Firewall is a "next-gen" "firewall." There are also host-based "firewalls" that run on the local host computer.
The "Firewall" app itself is a traditional firewall used to block and/or flag TCP and UDP sessions passing through NG Firewall using rules. The Firewall app provides the same functionality as the traditional "firewall" - the ability to use rules to control which computers and communicate on a network.
Settings
This section reviews the different settings and configuration options available for Firewall.
Status
This displays the current status and some statistics.
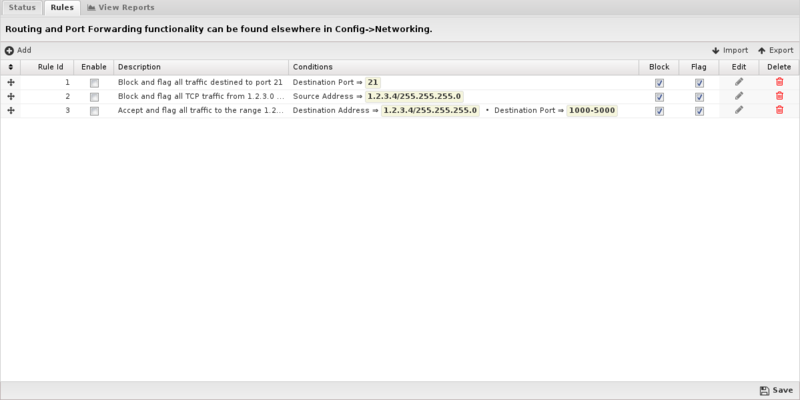
Rules
The Rules tab allows you to specify rules to Block, Pass or Flag traffic that crosses the NG Firewall.
The Rules documentation describes how rules work and how they are configured. Firewall uses rules to determine to block/pass the specific session, and if the sessions is flagged. Flagging a session marks it in the logs for reviewing in the event logs or reports, but has no direct effect on the network traffic.
Typically NG Firewall is installed as a NAT/gateway device, or behind another NAT/gateway device in bridge mode. In this scenario all inbound sessions are blocked by NAT except those explicitly allowed with port forwards. Because of this, the Firewall does not block anything by default. It is up to you to decide to best fit for your network, whether you only want to block specific ports or you want to block everything and allow only a few services.
Rule Actions
- Pass: Allows the traffic which matched the rule to flow.
- Block: Blocks the traffic which matched the rule.
Additionally a session can be flagged. If Flag is checked the event is flagged for easier viewing in the event log. Flag is always enabled if the action is Block.
Reports
The Reports tab provides a view of all reports and events for all traffic handled by Firewall.
Reports
This applications reports can be accessed via the Reports tab at the top or the Reports tab within the settings. All pre-defined reports will be listed along with any custom reports that have been created.
Reports can be searched and further defined using the time selectors and the Conditions window at the bottom of the page. The data used in the report can be obtained on the Current Data window on the right.
Pre-defined report queries: {{#section:All_Reports|'Firewall'}}
The tables queried to render these reports:
Related Topics
Firewall FAQs
Can I use multiple IP addresses in a single rule?
You can add multiple IPs to a rule using comma-separated values, with no spaces. These values can include single IPs, hyphen-separated ranges, or network spaces using CIDR. The string "1.1.1.1,2.2.2.2-3.3.3.3,4.4.4.0/24" is a valid string for rules.
How does NG Firewall know the geographical location of an IP address?
NG Firewall uses a tool called GeoIP2 by Maxmind to determine an IP address' physical location in the world. More details about that service are available here: https://www.maxmind.com/en/geoip2-services-and-databases
Why doesn't the Firewall app have any rules enabled by default?
When NG Firewall is in router mode, it is performing NAT, which blocks all inbound sessions. When NG Firewall is in bridge mode, the NG Firewall is already behind a firewall, which is doing NAT.
The default is pass all?! Why? That's so insecure!
As explained above, most NG Firewall boxes are install in router mode meaning that NAT is being performed on traffic. This means all inbound traffic is blocked regardless of the settings in the Firewall, only explicitly port forwarded traffic goes inside your network. Alternatively, most bridge mode deployments are installed behind a NAT device so the Firewall app (and NG Firewall) will only see traffic that has already explicitly been passed with a port forward on the NAT device. What this means is that the "pass all" default in most scenarios means "block everything inbound but nothing outbound", which is common policy for a lot of organizations. In our opinion most of the Firewall's utility is for controlling outbound traffic, however you are free to add rules controlling inbound, outbound or any other type of traffic you wish.
Where do I add Port Forwards?
Port forwarding is a feature available in Config > Network > Port Forward Rules.
I want to lock-down my network but for a few exceptions. What is the best way to do this?
Simply add a rule with no qualifiers, set it to Block, and put it at the bottom of the list. This will match all traffic, so anything not explicitly passed in a rule above it will be blocked.
Why are my Firewall rules not being triggered?
Firewall rules work from top to bottom; the first rule that the traffic matches will fire. If you have a broad rule near the top of your list that is matching, no other rules will be evaluated.
Should I use pre-NAT or post-NAT addresses/ports in firewall rules?
Firewall rules always match on the address which has more information. In other words if the entire internal network is being NATd from 192.168.*.* to 1.2.3.4, Firewall will match on the 192.168.*.* for traffic to and from this network. At the session layer this works out to be pre-NAT on source address, post-NAT on destination address, pre-NAT on source port, and post-NAT on destination port. An easy way to remember this is that it always matches where it gets the most information.
I'm trying to use Firewall to filter NG Firewall administration access or SSH or local services. It's not working, why?
Firewall processing only TCP and UDP sessions going *through* NG Firewall. In order to filter/control sessions going to NG Firewall itself you will need to use Access Rules in Config > Network > Advanced > Access Rules.
Does Firewall use iptables?
No. Firewall has nothing to do with iptables. Firewall rules are not iptables rules.
