Reports: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 129: | Line 129: | ||
If you are having problems adding a specific alert, or have common alert rules you would like added to the default rules, let us know on the forums or through the support team. | If you are having problems adding a specific alert, or have common alert rules you would like added to the default rules, let us know on the forums or through the support team. | ||
=== Email === | === Email Templates === | ||
You can customize emailed reports using Report Templates. You can create as many as you wish with any combination of: | You can customize emailed reports using Report Templates. You can create as many as you wish with any combination of: | ||
Revision as of 19:29, 13 December 2016
| File:Reports 128x128.png Reports |
|
About Untangle Reports
Reports provides users with detailed statistics of the traffic and activity on your network.
These reports can be viewed online, either through the administration interface or through the separate reporting interface available to non-administrators reporting-only users.
Report summaries can be sent via email, which includes basic information and a link to view the online reports if the user has access.
Reports can backup your data in multiple formats to Google Drive for long term storage.
Reports also contains alerts which can send you alerts in real-time when critical events occur.
Settings
This section reviews the different settings and configuration options available for Reports.
Status
On this tab you can click View Reports to open up Reports in a new browser tab.
Manage Reports
Here you can manage the reports that are displayed in each application. Each report is broken out by category and listed in the same display order you will find on the corresponding reports tab.
With the Enabled check box, you can remove reports from the display within each app. This will remove reports from the Reports tab without deleting the report, useful for unused reports.
View can be used to bring up any report without leaving the Reports app. This is useful for easily viewing and comparing reports across different apps.
Edit is a very powerful tool, allowing you to manipulate nearly every aspect of a report.
You can also use the Edit button to copy a report as well. This allows you to keep the original report while also having a customized version to meet your needs. Click Edit, then Copy Report. Update the report title and other fields as necessary.
For custom reports, the Delete button can be used to permanently delete a report. Note that Untangle pre-defined reports can not be deleted from the system.
Data
- Data Retention: This value controls how much time report data is kept on disk. Please note that increasing the number increases the amount of disk space that is needed for data storage.
- 'Upload Data to Google Drive If enabled, and the Google Connector in Directory Connector is enabled, your daily data will be uploaded to google drive each night for safe storage.
- 'Upload CSVs to Google Drive If enabled, and the Google Connector in Directory Connector is enabled, your daily CSV files will be uploaded to google drive each night for safe storage.
- Google Drive Directory configures which subdirectory data will be uploaded to in google drive.
- Import/Restore Data Backup Files imports data from a previous backup into the database. NOTE: this directly imports the SQL contents. If you have upgraded and the database schema has significantly changed since the time of the back, the import will not work correctly.
Alert Rules
Alert rules are evaluated on all events logged in the database and will log and/or alert the administrator when interesting or noteworthy events occur.
Each logged event is represented by a JSON object. As each event is logged to the database the alert rules are evaluated. The Event Logging page details all of the logging events. If all of an alert rule's conditions match the logged event the action(s) configured in the alert rule is performed.
Enable Thresholds limits the alert from firing until it reaches a certain frequency threshold.
Exceeds Threshold Limit is the frequency limit for which this condition will match. If the frequency is greater than this value, then the threshold conditions matches.
Over Timeframe defines the time range, in seconds, to use to compute the frequency.
Grouping Field defines how to group thresholds by an attribute field in the events. This field is optional.
If Exceeds Threshold Limit is 100 and Over Timeframe is 60, then the threshold condition will only match when this rules other conditions match approximately 100 times over any 60 second period. If Group Field is set to "CClientAddr" then the threshold load is grouped by "CClientAddr" value in the event objects. Using the above example this would mean that the alert would only fire when a specific "CClientAddr" like "192.168.1.100" does something over 100 times within 60 seconds. The threshold value for other clients like "192.168.1.150" is tracked separately.
Log Alert logs the event to the Alert Event Log
Send Alert sends an email to all administrators' emails describing the event.
Limit Send Frequency limits the number of times a rule can send an alert email To once per the configured amount of minutes. For some cases, like a low disk space alert, this is useful to limit the number of alerts sent so that an alert is not sent every minute.
Adding Alert Rules
Since alerts are created on the raw messages passed through the system before logging, adding alerts can be a bit tricky. An example is helpful to describe how alert rules are created.
One of the included alert rules is the "WAN is offline" alert. This triggers whenever a WAN interface has been disconnected.
In the conditions, you can see we are looking for two Field conditions. All conditions for alert rules will be field conditions, which simply means an entry in the logged event represented by a JSON object (there are no other choices in the drop down). In nearly all cases you will have a field condition with a class, which represents an application or system process responsible for logging and one or more additional conditions to alert.
Going back to our example, you can see the alert rule is monitoring the class WanFailoverEvent which is created by WAN Failover. Within that class we are looking for any log event object that contains an action = DISCONNECTED. In this case that means a WAN was found to be disconnected by WAN Failover and an alert is triggered.
You can view the Event Logging page for various classes and conditions that can be monitored for alert events.
If you are having problems adding a specific alert, or have common alert rules you would like added to the default rules, let us know on the forums or through the support team.
Email Templates
You can customize emailed reports using Report Templates. You can create as many as you wish with any combination of:
- Interval: Daily, Weekly, Monthly. You can only use an interval that matches your Data retention days. So if you have 7, you can only do Daily or Weekly, not Monthly.
- Mobile: Generate chart images more appropriate for a mobile device.
- Reports: Select those reports under Config and Application sections. Text and chart reports are allowed but not event list reports. Reports for applications will be included only if that application is installed.
Additionally, you can copy the settings for an existing report.
The default Daily Reports template includes common text and chart reports for your system. This template is fixed and cannot be changed or modified.
Email Templates must be associated with Report Users.
Syslog
Reports supports the sending of all events via syslog messages. To use syslog simply install a syslog receiver on another server, then enable syslog and configure as necessary.. Some syslog products are easier to set up than others. Kiwi, a third-party syslog daemon, is a favorite of many Untanglers using Windows, while those on *nix can use rsyslog.
- Host: The host name or IP address of the Syslog daemon that is authorized to receive syslog messages from the Untangle Server. Do not set the Host to the Untangle box itself - this will result in the hard drive filling up very quickly and most likely crashing the box.
- Port: The UDP port to send syslog messages to the syslog daemon. 514 is the default as this is the default syslog port.
- Protocol: The protocol to use to send syslog messages. The default is UDP.
WARNING: Syslog sends every single event to your syslog server. This is a very expensive operation, consuming both processing power and bandwidth. Syslog should only be used in special circumstances when something is actually done with the data on the syslog server.
Name Map
You can use the Name Map to manually configure the hostname for hosts. Untangle often can automatically determine the hostname for the IP automatically via DHCP or other methods. You can view the current names for currently active hosts in the Host Viewer
However, when Untangle is unable to automatically determine a hostname for an IP the Name Map provides a way to manually name them.
Accessing Reports
If a user is set up to receive email reports, they only need to view or download the HTML attachment to see an overview report. If they need more information or would like to drill down to specific users or machines, they can use the link in the email, which will open Reports on the Untangle if it is accessible from their location. Administrators can use the View Reports button in Reports settings to open the Reports.
To access Reports directly from a browser, you have two options:
- Outside the Untangle's network: Browse to the IP of the Untangle /reports using HTTPs, such as https://192.0.2.1/reports.
- Inside the Untangle's network: Browse to the IP of the Untangle /reports, such as http://192.168.1.1/reports.
Please note that to view Reports from outside the network you'll need to check Allow HTTPS on WANs at Config > Network > Advanced > Filter Rules. If you have changed the External HTTPS Port, you'll need to use the proper HTTPS port when connecting from the outside.
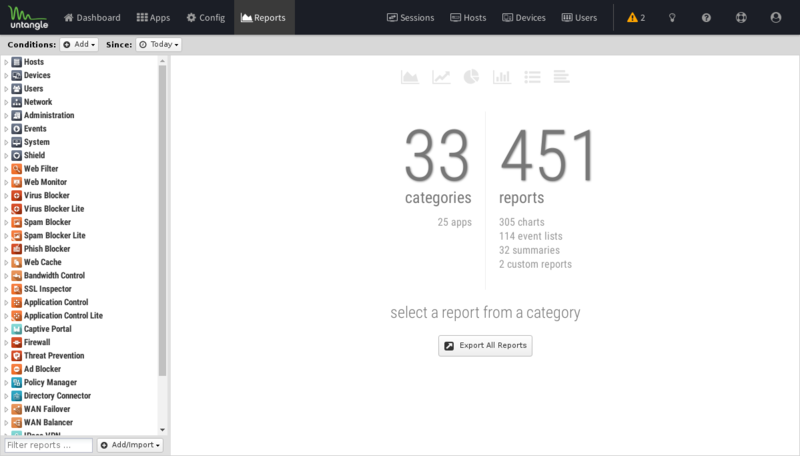
Report Viewer
Reports provide a graphical view of the network traffic and actions of your NG Firewall. Various reports are available within applications and base system components. The reports can be manipulated to drill down, customize, and export data in many ways using the Report Viewer.
There are a few panels in the Report Viewer:
- The top panel: This top panel (just below the navigation menu) allow you specify which data is viewed. By default, there is just a timeframe and no conditions, so reports will show all data for the specified timeframe. Conditions can be viewed to view more specific data, such as a specific host, user, domain, application, web category, etc.
- The left panel: This allows you to choose the report you wish to view. At the bottom you can use the search box to quickly find reports with the specified string in the title. You can also import and create new reports using the "Add/Import" button.
- The chart panel: This panel shows you the specified report. It also includes several action buttons at the top.
- The data panel: The data panel, hidden by default, can be displayed by clicking on the "Data View" button in the chart panel. This will show the raw data used to generate the chart and allow the user to export the data by clicking the "Export Data" button at the bottom.
Conditions
The Conditions panel appears at the top panel and can be used to filter data displayed in reports. For example, to view a "specific" host's report, you can add a condition for Client = "192.168.1.100" and then all reports available will only show data where the client is 192.168.1.100. Multiple conditions can be added to drill down and inspect data. Conditions can also be added quickly by clicking on slices in pie charts.
The Add Condition dropdown contains many commonly used conditions, or the full list of all tables and columns can be browsed by clicking on the "More" button to add conditions for any database column.
Note: Conditions will not apply to all reports. For example, If viewing a specific users report by adding a condition where Username = foobar - many reports will be greyed out and unviewable. This is because the data used to generate those reports is not relevent to the specific user (it does not contain a username column). For example, the CPU usage report is a system report that is not relevant to a specific network user and so there is no way to filter that data by user.
Condition Operators
The second field in the condition is the logical operator that will be used in evaluating the condition value defined in the last field. In most use cases the default "=" operator is what you want to use. However, there are several other operators available that make the reports and alerts a whole lot more powerful.
Conditions Example - Policy by Policy ID
In many cases, you may just want to see the traffic related to a specific policy within Policy Manager. This can be accomplished very easily by adding a condition using the Quick Add feature.
- In the Conditions panel, select Add.
- Choose Policy ID and specify equals and the policy ID in question.
- The conditions is applied and will remain applied as you switch between reports.
Conditions Example - Web Filter Categories
From pie charts, you can quickly add a condition from the Current Data window. This can be handy for use with the Web Filter category selection which we'll use for this example. Once the condition is applied, we can then use other reports to drill down to find out more information about the traffic such as which user might be responsible.
- Open Report Viewer or the Web Filter Reports tab.
- Select the Top Categories report (by size or requests). In our example, you can see Games was at the top.
- Click on the Games pie slice, and when prompted to add a condition click Yes.
- All Reports can now be viewed for Games only traffic.
- For example, the Top Clients (by request) will show the clients that visited the most gaming sites.
- For exmaple, the Web Usage (scanned) will show "Gaming" web usage throughout the day of the network.
Related Topics
Reports FAQs
What is the difference between Reports and Events?
Events and Reports are now the same. They provide real-time data for each individual application. The Events view will show the individual events that make up the reports, while reports will show a graphical interpretation of summarized events.
Why is Reports taking up all of my server's resources?
Check your Data Retention setting - if it's too high it will cause a lot of issues. Try setting it to the default of 7 to see if that helps.
Why am I not receiving an email with my Reports? 💡
If NG Firewall is set to email you and you're not receiving the emails, try the Email Test at Config > Email - if you get the test mail successfully, you should also get the email from Reports. If not, you can check /var/log/exim4/mainlog and look for the error, or contact Support.
I just upgraded my NG Firewall and my reports are missing. Why? 💡
An update may have changed how Reports stores data - the next time scheduled reports are run the report index will be rebuilt, which will allow you to access the older data. Please allow one complete reporting cycle (Daily, Weekly or Monthly) if you only run that type of report.
What is the "others" column when looking at the charts in Reports?
When looking at the Top 10 of a Reports chart, others is made up of everything else not listed. You can see the Top 9 sites visited by users in a day, while others is there to give us a baseline, for example if we saw one or two users with a larger percentage than others, we'd probably want to do some investigating as to why that user is pushing more web traffic than a large portion of the organization (relative to total organization size).
The spam and phishing stats don't seem to add up. Why?
You may notice that Reports contains a certain number of phish or spam email, however the Event Logs/CSVs show a different number. This is because the graphs show the actual number of emails while the Event Logs/CSVs treat each recipient as an individual email so per-user/host reports are correct. An example is a single spam email sent to two users - it will only be counted as one (email) in the Reports, but two (delivered emails) in the Event Logs/CSVs.
Why is the timestamp column not displayed properly in Excel when I open the CSV?
To solve this please change the format of the first column to the Date format.
Can reports users change their password?
Reports users cannot change their own password. They must contact the administrator to update the password on their behalf.
