Configuring NG Firewall for AWS using routed subnets: Difference between revisions
Bcarmichael (talk | contribs) |
Bcarmichael (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 48: | Line 48: | ||
#Click '''Yes, Create'''. | #Click '''Yes, Create'''. | ||
== Step 5. Attach the network interface == | == Step 5. Attach the network interface == | ||
After you create a network interface you must attach it to an instance. | [[File:Aws_attach_iface.png|thumb|right|upright=1.3|Attaching a network interface to an instance in AWS]]After you create a network interface you must attach it to an instance. | ||
#In the Network Interfaces screen select an available interface that belongs to the internal subnet. | #In the Network Interfaces screen select an available interface that belongs to the internal subnet. | ||
#In the Actions menu choose Attach. | #In the '''Actions''' menu choose '''Attach'''. | ||
#Select the Instance ID of your NG Firewall | #Select the Instance ID of your NG Firewall | ||
#Repeat the steps for creating and attaching network interfaces for all instances that you intend to place on the internal subnet. | #Repeat the steps for creating and attaching network interfaces for all instances that you intend to place on the internal subnet. | ||
{{Note|text=If you attach a new network interface to an instance other than NG Firewall, it is recommended to detach the previous network interface to prevent traffic from bypassing NG Firewall. To detach an interface, select the network interface and choose '''Detach''' from the '''Actions''' menu. }} | |||
==<span style="color: #000000; font-weight: 400; text-decoration: none;">Routes</span>== | ==<span style="color: #000000; font-weight: 400; text-decoration: none;">Routes</span>== | ||
Revision as of 23:31, 30 August 2018
Overview
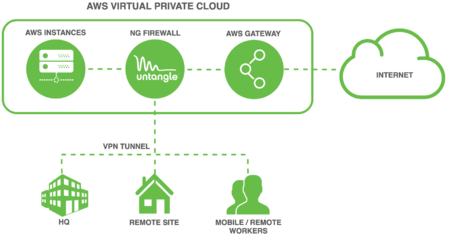
Untangle NG Firewall deployment in AWS can secure Internet access for other AWS instances. This scenario is useful if you have for example Amazon Workspaces and you need to apply Intrusion Prevention, Content Filtering, Bandwidth Control, and other next generation firewall capabilities to those instances. This type of deployment requires advanced Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) configuration to establish an internal subnet for AWS instances that routes through NG Firewall.
Before you begin
- Follow the steps outlined in Deploying NG Firewall in AWS.
- Review VPCs and Subnets in the AWS documentation.
Step 1. Configure a Security Group
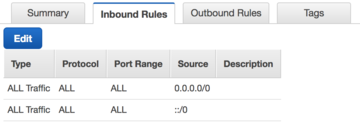
AWS instances and network interfaces inherit traffic rules defined by security groups. The security group assigned to your NG Firewall instance and instances on the private network behind NG Firewall should have an open policy to avoid conflicts. Confirm that the security group designated for your instances has rules to permit all incoming and outgoing traffic.
- In the AWS Management Console go to your VPC configuration from the Services menu.
- Click Security Groups.
- Select the default security group or a custom security group you designate for instances belonging to your internal subnet.
- In the Inbound Rules tab, click Edit.
- Add or confirm a rule allowing all traffic for all protocols where the source is 0.0.0.0/0.
- Confirm this same policy in the Outbound Rules tab.
Step 2. Configure a Network ACL
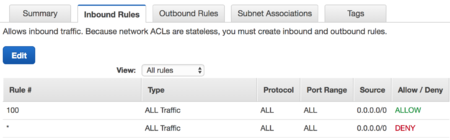
Each subnet inherits the policies of network ACLs. Confirm that the network ACL designated for your internal subnet contain rules to permit all incoming and outgoing traffic.
- In the AWS Management Console go to your VPC configuration from the Services menu.
- Click Network ACLs.
- Select the default network ACL or a custom network ACL if designated for your internal subnet.
- In the Inbound Rules tab, click Edit.
- Add or confirm a rule allowing all traffic for all protocols where the source is 0.0.0.0/0.
- Confirm this same policy in the Outbound Rules tab.
Step 3. Create an internal subnet
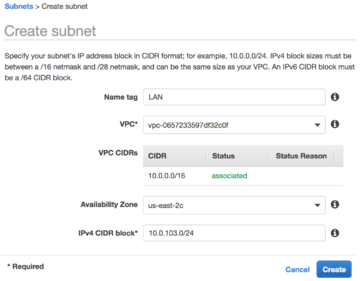
To route traffic for AWS instances through NG Firewall you must designate an internal [subnet]. You assign this subnet to network interfaces belonging to your AWS instances and NG Firewall.
- In the [AWS Management Console] go to your VPC configuration from the Services menu.
- Click Subnets.
- Click Create Subnet.
- Select the VPC containing your NG Firewall and AWS instances.
- Select an availability zone.
- Assign an IPv4 block that is within the scope of your VPC.
- Click Create to confirm the new subnet.
Step 4. Create a network interface
Network interfaces in AWS attach to instances and facilitate network access to the VPC. The NG Firewall and instances protected by the firewall must be assigned to the internal subnet you created in the previous step. If you created your instances and network interfaces prior to creating the internal subnet, you can create new network interfaces to associate your instances to the internal subnet.
- In the AWS Management Console go to your EC2 configuration from the Services menu.
- Click Network Interfaces.
- Click Create Network Interface.
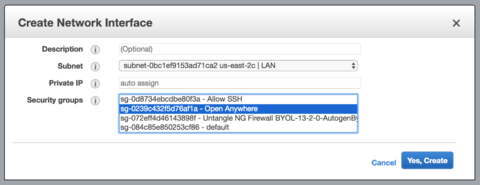
AWS network interface configuration wizard - Select the internal subnet you created in the previous step.
- Keep Private IP as auto assign.
- Select the permissive security group you created in the first step.
- Click Yes, Create.
Step 5. Attach the network interface
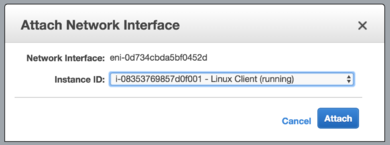
After you create a network interface you must attach it to an instance.
- In the Network Interfaces screen select an available interface that belongs to the internal subnet.
- In the Actions menu choose Attach.
- Select the Instance ID of your NG Firewall
- Repeat the steps for creating and attaching network interfaces for all instances that you intend to place on the internal subnet.
Routes
Create a new route table and add a default route using the internal network interface you’ve created:
Navigate to Services → VPC → Route Tables
Select “Create Route Table”
- Set a Name Tag for the Route: e.g. Untangle - Private
- Select the VPC the Untangle is in: e.g. vpc-79ceo5f0
- Add the default route and attach it to the internal network interface:
- Select the route table you just created
- Select the Routes tab and then the “Edit” button
- Destination: 0.0.0.0/0
- Target - select the internal Network Interface you created: e.g. eni-f360b9e4
- Select the “Save” button.
- Next, select the Subnet Associations tab and select the “Edit” button:
- Select the internal subnet
- The select the “Save” button:
Create Internet Gateway
The VPC must have an Internet Gateway. Most VPC will already have one pre-configured. If one does not exist, create one:
- Navigate to Services → VPC → Internet Gateway
- Select “Create Internet Gateway” button
- Enter a Name tag: e.g. VPI -IGW
- Select the “Save” button
Launch the Untangle - AMI
- Navigate to Services → EC2 → Select the Launch Instance Button
- Select AWS Marketplace and search for Untangle
- Select the “Launch” button for the Untangle NG Firewall
- Select the Instance type
- Select the “Next: Configure Instance Details"
- Subnets: Select the External Subnet you created:
- Select the “Add Device” Button
- Set eth1 to the Internal Subnet you created
- Select the “Next: Add Storage” Button
- Select the “Next: Add Tags” Button:
- Tags - You can add tags to help you identify the AMI / Resources
- Select the “Next: Configure Security Group” button:
- Configure Security Group:
- Choose the “Select existing Security Group” radio button
- Choose the Security group you configured:
- Select the “Review and Launch” button:
- Subnets: Select the External Subnet you created:
- Review your configuration - Make any adjustments if needed:
- Select the “Launch” button:
- Key Pair
- Select an existing key pair or create new one
- Select “Launch Instance” button
Check your Untangle Instance
- Navigate to Services → EC2 →
- Verify the Instance is running
- Make note of the Public IP
- Login to Untangle
- Point your browser at: https://<publicIP> e.g.: https://34.22.127.3
- Configure Untangle
Your browser may show a message indicating that connecting to your new server needs caution. This message is simply telling you that there isn't yet a server certificate in place because the server is not yet configured. Once the Untangle setup process is complete, this warning will no longer occur when you direct a browser to your new server.