Dynamic Routing: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<span style="display:none" class="helpSource network_dynamicrouting"> | <span style="display:none" class="helpSource network_dynamicrouting">Dynamic Routing</span> | ||
<span style="display:none" class="helpSource network_advanced_dynamicrouting"> | <span style="display:none" class="helpSource network_advanced_dynamicrouting">Dynamic Routing</span> | ||
== About Dynamic Routing == | == About Dynamic Routing == | ||
Revision as of 17:45, 13 March 2018
About Dynamic Routing
Dynamic Routing allows for the exchange of routes between other routers using Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF).
Dynamic Routing settings can be found at Config > Network > Advanced > Dynamic Routing.
BGP Overview
The Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) requires that all nodes known as neighbors are known and added to the settings.
OSPF Overview
Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) does not require all nodes to be known. Instead each route is associated with a group called an area. OSPF can be hierarchical through the use of multiple areas so some networks are publicly known and others can be private. Additionally OSPF supports authentication.
Settings
This section reviews the different settings and configuration options available for Dynamic Routing.
- Dynamic Routing Enabled: Controls whether dynamic routing is enabled or disabled. The default setting is unchecked, which means dynamic routing is disabled. BGP and/or OSPF must also be enabled as well.
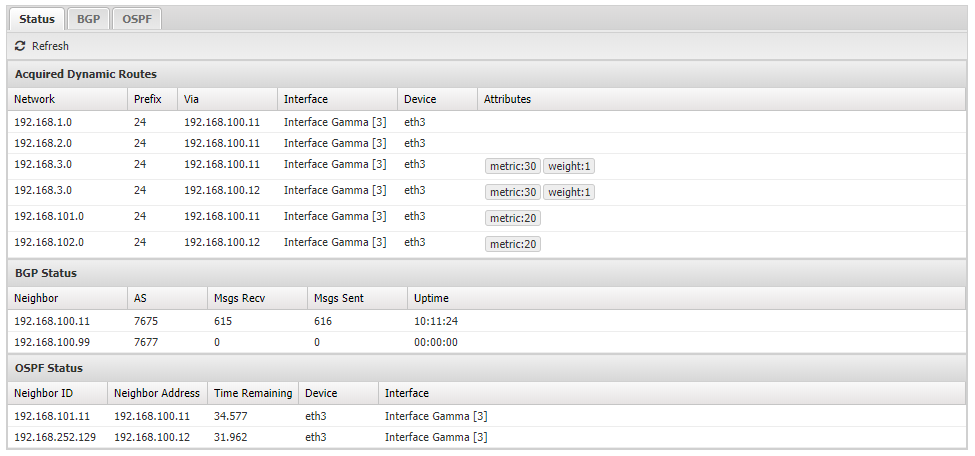
- Status: Overall status of dynamic routing shows:
- Acquired Dynamic Routes: All routes obtained from enabled dynamic routing protocols.
- BGP Status Information about each BGP neighbor including messages received, sent, and uptime.
- OSPF Status Information about discovered OSPF neighbor such as their IP address and the time remaining until they next synchronize.
- BGP: Enable BGP protocol.
- Router ID: An IP-like identifier. It can be any IP-address like value but is typically your WAN address.
- Router AS: The Autonomous System (AS) number for this system. It can be any number from 1-65535 but must be unique in your BGP network.
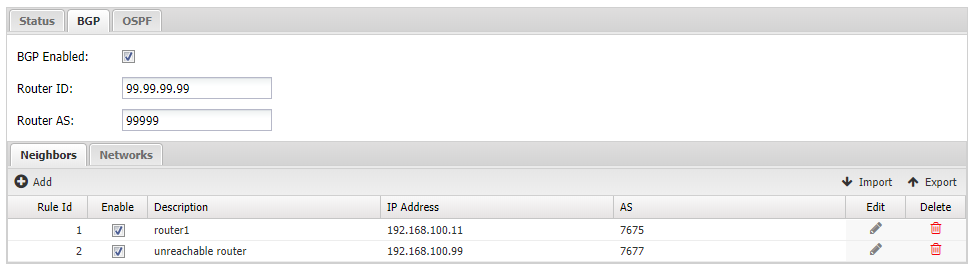
- Neighbors Define each BGP neighbor here. For each neighbor, you will need to know their IP address and AS.
- Networks Define each local network route to share via BGP.
- OSPF: Enable OSPF protocol.
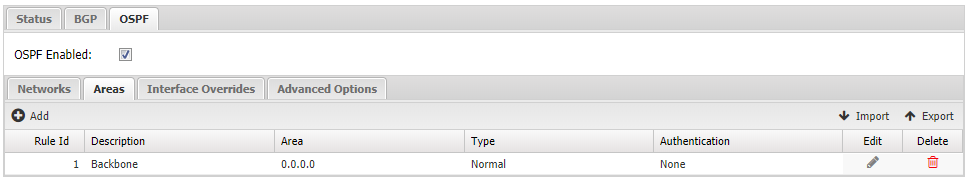
- Networks Define each local network route to share via OSPF.
- Areas Define OSPF areas. The default area 0.0.0.0 is already defined. It may be modified and others may be added as needed for your network.
- Interface Overrides Under certain conditions you may need to override default settings for OSPF interfaces. Most notably, if yo wish to enable authentication on an area you will need to specify the type of authentication on a specific interface.
- Advanced Options Here you can override OSPF defaults.