Deploying NG Firewall in Amazon AWS: Difference between revisions
Bcarmichael (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
|||
| (42 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
== Overview == | == Overview == | ||
NG Firewall supports deployment via [https://aws.amazon.com Amazon Web Services] (AWS). NG Firewall for AWS is a 64-bit Amazon Machine Image (AMI) that is launched and managed from the [https://aws.amazon.com/console AWS Management Console]. This deployment option is useful for example in decentralized network environments that need to route through a remote gateway to enforce policy management, reporting, content filtering, and other types of network security. | |||
== Before you begin == | |||
You need a valid AWS account before you can deploy NG Firewall in AWS. If you do not have an AWS account you can register [https://portal.aws.amazon.com/billing/signup#/start here]. | |||
== Getting Started == | == Getting Started == | ||
=== Step 1: Select an instance type === | === Step 1: Select an instance type === | ||
Before launching | Before launching NG Firewall for AWS, it is necessary to determine the type of licensing model and infrastructure that is appropriate for your intended usage. | ||
==== Licensing ==== | ==== Licensing ==== | ||
NG Firewall for AWS is available as either a Pay-As-You-Go (PAYG) subscription or Bring-Your-Own-License (BYOL). The PAYG option combines the cost of software licensing and infrastructure into one monthly bill. The BYOL option enables you to deploy an unlicensed version of NG Firewall for AWS. | |||
Both licensing options require the selection of AWS infrastructure in the form of an instance type. The available instance types and their associated costs are outlined in the Pricing Information section of the AWS Marketplace Overview page. Refer to the following links: | |||
*[https://aws.amazon.com/marketplace/pp/B07F9W38V1 NG Firewall PAYG] | |||
*[https://aws.amazon.com/marketplace/pp/B07BSPV2S9?qid=1531347434223 NG Firewall BYOL] | |||
==== Infrastructure ==== | ==== Infrastructure ==== | ||
AWS instances are available in different sizes to accommodate the performance requirements of your deployment. | AWS instances are available in different sizes to accommodate the performance requirements of your deployment. The table below provides general guidance to help you identify which instance type to choose based on your intended usage. | ||
The table below provides general guidance to help you identify which instance type to choose based on your intended usage. | |||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 14: | Line 22: | ||
! Specifications | ! Specifications | ||
! Max devices (suggested) | ! Max devices (suggested) | ||
! Installed apps | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Small | | Small | ||
| 1 vCPU core | | 1 vCPU core | ||
2 GB memory | 2 GB memory | ||
| Up to | | Up to 25 devices | ||
| IPsec VPN, Directory Connector, Firewall, Threat Prevention, Web Filter, Policy Manager, Configuration Backup, Bandwidth Control, Captive Portal | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Medium | | Medium | ||
| 2 vCPU cores | | 2 vCPU cores | ||
4 GB memory | 4 GB memory | ||
| Up to | | Up to 100 devices | ||
| All apps | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Large | | Large | ||
| Line 29: | Line 40: | ||
8 GB memory | 8 GB memory | ||
| Up to 500 devices | | Up to 500 devices | ||
| All apps | |||
|- | |- | ||
| Extra Large | | Extra Large | ||
| Line 34: | Line 46: | ||
16 GB memory | 16 GB memory | ||
| Up to 5000 devices | | Up to 5000 devices | ||
| All apps | |||
|} | |} | ||
=== Step 2 | |||
=== Step 2: Prepare your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) === | |||
A VPC is the virtual networking environment where your AWS instances reside. The quickest way to deploy NG Firewall for AWS is to launch the instance into the default VPC. In the [https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AmazonVPC/latest/UserGuide/default-vpc.html default VPC configuration] AWS automatically configures the required components including the gateway, subnets, and routing. | |||
A VPC is the virtual networking environment where your AWS instances reside. The quickest way to deploy | {{Note|text=For advanced scenarios involving custom VPCs and routing via network interfaces, refer to [[Configuring NG Firewall for AWS using routed subnets]].}} | ||
{| | |||
=== Step 3: Add a subscription === | |||
[[File:untangle-aws-subscribe.png|thumb|upright=1.2|alt=Untangle NG Firewall listing in AWS marketplace|Arista ETM NG Firewall subscription listing in AWS marketplace]]After you choose a licensing option and instance type, you can add the subscription to your AWS account. To add the subscription: | |||
#Navigate to the [https://aws.amazon.com/marketplace/seller-profile/ref=dtl_pcp_sold_by?ie=UTF8&id=6d421c85-26c9-48c7-be13-70e71f5e1bd2 Arista ETM NG Firewall marketplace listing]. | |||
=== Step | #Select either PAYG or BYOL. | ||
#Click '''Continue to Subscribe'''. | |||
[[File: | #Click Continue to configuration. | ||
# | #Select your '''Fulfillment option''', '''Software version''', and '''Region'''. | ||
#Click ''' | #Click '''Continue to launch'''. | ||
# | #Beneath '''Choose action''', select Launch through EC2. | ||
# | #Click '''Launch'''. | ||
# | |||
=== Step 4: Configure the NG Firewall Instance === | |||
[[File:Untangle-aws-step1.png|thumb|right|upright=1.4|NG Firewall AMI listing in AWS marketplace]] | |||
After you launch the instance from the marketplace using the Launch through EC2 option, AWS directs you to the instance configuration wizard in the EC2 Management Console. | |||
#Confirm the instance type that suits your needs and click '''Next: Configure Instance Details'''. | |||
#If necessary, adjust the settings of your instance. For simple deployment, make sure the '''Network''' matches your default VPC and click '''Next: Add Storage'''. | #If necessary, adjust the settings of your instance. For simple deployment, make sure the '''Network''' matches your default VPC and click '''Next: Add Storage'''. | ||
#If necessary, increase the storage '''Size''' and click '''Next: Add Tags'''. | #If necessary, increase the storage '''Size''' and click '''Next: Add Tags'''. | ||
#If necessary, assign a tag to help you identify and manage this instance. Click '''Next: Configure Security Group'''. | #If necessary, assign a tag to help you identify and manage this instance. Click '''Next: Configure Security Group'''. | ||
#Select '''Create new security group''' and assign it a name and description. Set the '''Type | #Select '''Create new security group''' and assign it a name and description. Set the '''Type''' to “All traffic” and Source to “Anywhere”. Click '''Next: Review and Launch'''. | ||
#Review the summary of your instance and click '''Launch'''. | #Review the summary of your instance and click '''Launch'''. | ||
'''NOTE:''' The default storage size is 8 GiB, which is sufficient for lite usage. Increase the storage size in the '''Add Storage''' step if you expect more than 50 hosts or if you wish to retain reporting data beyond the default value of seven days. Refer to the [[Performance Guide]] for tips to reduce the system requirements. | |||
=== Step 5: Allocate a static IPv4 Address === | === Step 5: Allocate a static IPv4 Address === | ||
AWS maps Internet routable IPv4 addresses to your instances dynamically from a pool of addresses. This means that the Internet routable IPv4 address assigned to your instance might change after a reboot or lease expiration. To ensure that your instance maintains the same IPv4 address, you can allocate an [https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/elastic-ip-addresses-eip.html Elastic IP Address]. | AWS maps Internet routable IPv4 addresses to your instances dynamically from a pool of addresses. This means that the Internet routable IPv4 address assigned to your instance might change after a reboot or lease expiration. To ensure that your instance maintains the same IPv4 address, you can allocate an [https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/elastic-ip-addresses-eip.html Elastic IP Address]. | ||
#Navigate to the '''Elastic IPs''' area of the [https://aws.amazon.com/console EC2 Management Console]. [[File:Untangle-aws-elastic-ip.png|thumb|right|upright=1.1|Allocating an elastic IP]] | #Navigate to the '''Elastic IPs''' area of the [https://aws.amazon.com/console EC2 Management Console]. [[File:Untangle-aws-elastic-ip.png|thumb|right|upright=1.1|Allocating and associating an elastic IP]] | ||
#Click '''Allocate new address''' and continue through the prompts. | #Click '''Allocate new address''' and continue through the prompts. | ||
#Once the IPv4 address is allocated, select it from the list and click '''Actions''' → '''Associate address'''. | #Once the IPv4 address is allocated, select it from the list and click '''Actions''' → '''Associate address'''. | ||
#In the '''Associate address''' screen, select your | #In the '''Associate address''' screen, select your NG Firewall instance and click '''Associate'''. | ||
=== Step 6: Connect to your instance === | === Step 6: Connect to your instance === | ||
To connect to your instance: | To connect to your instance: | ||
#Review the status of your | #Review the status of your NG Firewall appliance in the '''Instances''' area of the [https://aws.amazon.com/console EC2 Management Console].[[File:Untangle-aws-instances.png|thumb|none|upright=1.3|Instances in AWS management console]] | ||
[[File:Untangle-aws-instances.png|thumb| | #Confirm the '''Instance State''' is “running”. | ||
#Confirm the Instance State is “running”. | #Take note of your '''Instance ID''' and '''Public DNS''' address. | ||
#Take note of your Instance ID and Public DNS address. | |||
#Open a new browser window and connect via HTTPS to your Public DNS address. | #Open a new browser window and connect via HTTPS to your Public DNS address. | ||
#Accept the self-signed SSL certificate and proceed to the URL. | #Accept the self-signed SSL certificate and proceed to the URL. | ||
#At the | #At the NG Firewall login prompt enter the '''Instance ID''' as the password and click '''Login'''. | ||
=== Step 7: Configure NG Firewall for AWS === | |||
After you log in to your NG Firewall for the first time, select the language and proceed with the initial configuration provided by the Setup Wizard. | |||
{{Note|text=For PAYG instances, you must authenticate prior to accessing the setup wizard. The default user is '''admin''' and your password is the Instance ID. }} | |||
==== Setup Wizard ==== | |||
#On the first step of the wizard, configure a new administrative password, notification email address, install type, and timezone. Click '''Network Cards''' to proceed. [[File:Untangle-setup-1.png|thumb|upright=1.3|none|Setup Wizard step one - Configure the server]] | |||
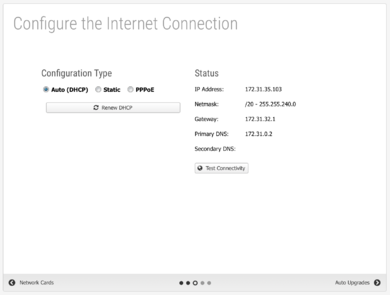
#On the '''Identify Network Cards''' step, choose '''Continue anyway'''. Click '''Internet Connection''' to proceed. [[File:Untangle-setup-2.png|thumb|upright=1.3|none|Setup Wizard step two - Identify network cards]] | |||
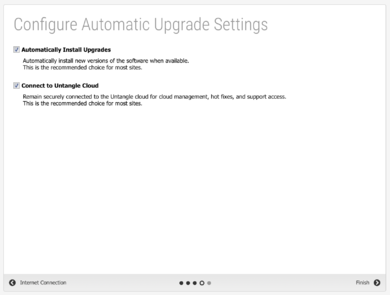
#On the '''Configure the Internet Connection''' step, confirm the '''Auto (DHCP)''' selection for the '''Configuration type''' and review the '''Status'''. Click '''Auto Upgrades''' to proceed. [[File:Untangle-setup-3.png|thumb|upright=1.3|none|Setup Wizard step three - Configure the Internet connection]] | |||
#On the Configure Automatic Upgrade Settings step, review the automatic upgrades and Cloud connection options. We recommend enabling both options. Click Finish to complete the wizard.[[File:Untangle-setup-4.png|thumb|upright=1.3|none|Setup Wizard step four - Configure automatic upgrade settings]] | |||
#If you selected '''Connect to Cloud''' in the final step of the setup wizard, follow the prompts to log in or set up your ETM Dashboard account to add the new appliance to your organization. | |||
{{Note|text=To simplify the VPC deployment, NG Firewall for AWS requires only a single network interface. The internal network interfaces associate to each VPN tunnel or connection.}} | |||
==== Internet Hostname ==== | |||
[[File:Untangle-aws-hostname.png|thumb|right|upright=1.3|Hostname settings in Network configuration]] | |||
Components such as location services, notifications, and VPN profiles require knowledge of the Internet routable IP address that associates to the external interface of your instance. In AWS, instances use privately routable IP addresses and do not attach directly to the Internet. Therefore you must configure the NG Firewall with an Internet hostname that resolves to your Internet routable IP address or Elastic IP. | |||
#From the NG Firewall web administration navigate to '''Config''' → '''Network'''. | |||
#In the '''Hostname''' field, set the unqualified part of your Public DNS. | |||
#In the '''Domain Name''' field, set the qualified part of your Public DNS. | |||
#Select the '''Use Hostname''' option. | |||
{{Note|text=You can set the Internet hostname using your own domain name. In this case configure your DNS with an Address Record (A) type that points to the Elastic IP address of your instance.}} | |||
==== VPN Server ==== | |||
After you complete the setup wizard you can begin the VPN configuration of NG Firewall for AWS. The VPN server enables remote hosts and networks to create a secure tunnel that routes traffic through the NG Firewall to access the Internet. | |||
#From the NG Firewall web administration navigate to '''Apps''' → '''OpenVPN'''. | |||
#In the '''Status''' tab, toggle '''OpenVPN is enabled'''.[[File:Untangle-openvpn.png|thumb|upright:1.4|none|OpenVPN status view]] | |||
#In the '''Server''' tab, check Server Enabled. | |||
#In the '''Server''' tab → '''Remote Clients''' tab, click '''Add''' to create a new profile. | |||
#Assign the parameter of the profile. See [[OpenVPN]] for additional information.[[File:Untangle-openvpn-remoteclients.png|thumb|none|upright=1.4|OpenVPN remote clients view]] | |||
{{Note|text=For VPN tunnels with other vendors that do not support OpenVPN, use IPsec. See [[IPsec VPN]] for additional information and configuration details. }} | |||
== Next Steps == | |||
After performing the initial configuration you are ready to fine tune your policies and set up VPN tunnels at remote sites. Here are some related topics to get your started: | |||
*[[Tunnel VPN]] | |||
*[[Firewall]] | |||
*[[Application Control]] | |||
*[[Web Filter]] | |||
*[[Reports]] | |||
*[[Policy Manager]] | |||
*[[Intrusion Prevention]] | |||
*[[Bandwidth Control]] | |||
Latest revision as of 18:21, 2 November 2022
Overview
NG Firewall supports deployment via Amazon Web Services (AWS). NG Firewall for AWS is a 64-bit Amazon Machine Image (AMI) that is launched and managed from the AWS Management Console. This deployment option is useful for example in decentralized network environments that need to route through a remote gateway to enforce policy management, reporting, content filtering, and other types of network security.
Before you begin
You need a valid AWS account before you can deploy NG Firewall in AWS. If you do not have an AWS account you can register here.
Getting Started
Step 1: Select an instance type
Before launching NG Firewall for AWS, it is necessary to determine the type of licensing model and infrastructure that is appropriate for your intended usage.
Licensing
NG Firewall for AWS is available as either a Pay-As-You-Go (PAYG) subscription or Bring-Your-Own-License (BYOL). The PAYG option combines the cost of software licensing and infrastructure into one monthly bill. The BYOL option enables you to deploy an unlicensed version of NG Firewall for AWS.
Both licensing options require the selection of AWS infrastructure in the form of an instance type. The available instance types and their associated costs are outlined in the Pricing Information section of the AWS Marketplace Overview page. Refer to the following links:
Infrastructure
AWS instances are available in different sizes to accommodate the performance requirements of your deployment. The table below provides general guidance to help you identify which instance type to choose based on your intended usage.
| Instance Type | Specifications | Max devices (suggested) | Installed apps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Small | 1 vCPU core
2 GB memory |
Up to 25 devices | IPsec VPN, Directory Connector, Firewall, Threat Prevention, Web Filter, Policy Manager, Configuration Backup, Bandwidth Control, Captive Portal |
| Medium | 2 vCPU cores
4 GB memory |
Up to 100 devices | All apps |
| Large | 2 vCPU cores
8 GB memory |
Up to 500 devices | All apps |
| Extra Large | 4 vCPU cores
16 GB memory |
Up to 5000 devices | All apps |
Step 2: Prepare your Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)
A VPC is the virtual networking environment where your AWS instances reside. The quickest way to deploy NG Firewall for AWS is to launch the instance into the default VPC. In the default VPC configuration AWS automatically configures the required components including the gateway, subnets, and routing.
| For advanced scenarios involving custom VPCs and routing via network interfaces, refer to Configuring NG Firewall for AWS using routed subnets. |
Step 3: Add a subscription
After you choose a licensing option and instance type, you can add the subscription to your AWS account. To add the subscription:
- Navigate to the Arista ETM NG Firewall marketplace listing.
- Select either PAYG or BYOL.
- Click Continue to Subscribe.
- Click Continue to configuration.
- Select your Fulfillment option, Software version, and Region.
- Click Continue to launch.
- Beneath Choose action, select Launch through EC2.
- Click Launch.
Step 4: Configure the NG Firewall Instance
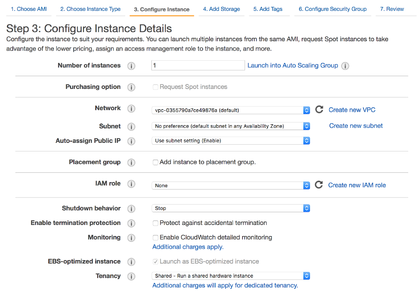
After you launch the instance from the marketplace using the Launch through EC2 option, AWS directs you to the instance configuration wizard in the EC2 Management Console.
- Confirm the instance type that suits your needs and click Next: Configure Instance Details.
- If necessary, adjust the settings of your instance. For simple deployment, make sure the Network matches your default VPC and click Next: Add Storage.
- If necessary, increase the storage Size and click Next: Add Tags.
- If necessary, assign a tag to help you identify and manage this instance. Click Next: Configure Security Group.
- Select Create new security group and assign it a name and description. Set the Type to “All traffic” and Source to “Anywhere”. Click Next: Review and Launch.
- Review the summary of your instance and click Launch.
NOTE: The default storage size is 8 GiB, which is sufficient for lite usage. Increase the storage size in the Add Storage step if you expect more than 50 hosts or if you wish to retain reporting data beyond the default value of seven days. Refer to the Performance Guide for tips to reduce the system requirements.
Step 5: Allocate a static IPv4 Address
AWS maps Internet routable IPv4 addresses to your instances dynamically from a pool of addresses. This means that the Internet routable IPv4 address assigned to your instance might change after a reboot or lease expiration. To ensure that your instance maintains the same IPv4 address, you can allocate an Elastic IP Address.
- Navigate to the Elastic IPs area of the EC2 Management Console.
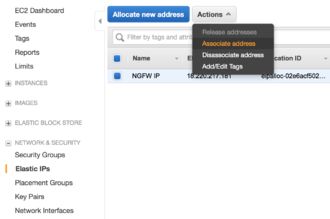
Allocating and associating an elastic IP - Click Allocate new address and continue through the prompts.
- Once the IPv4 address is allocated, select it from the list and click Actions → Associate address.
- In the Associate address screen, select your NG Firewall instance and click Associate.
Step 6: Connect to your instance
To connect to your instance:
- Review the status of your NG Firewall appliance in the Instances area of the EC2 Management Console.
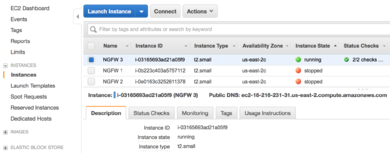
Instances in AWS management console - Confirm the Instance State is “running”.
- Take note of your Instance ID and Public DNS address.
- Open a new browser window and connect via HTTPS to your Public DNS address.
- Accept the self-signed SSL certificate and proceed to the URL.
- At the NG Firewall login prompt enter the Instance ID as the password and click Login.
Step 7: Configure NG Firewall for AWS
After you log in to your NG Firewall for the first time, select the language and proceed with the initial configuration provided by the Setup Wizard.
| For PAYG instances, you must authenticate prior to accessing the setup wizard. The default user is admin and your password is the Instance ID. |
Setup Wizard
- On the first step of the wizard, configure a new administrative password, notification email address, install type, and timezone. Click Network Cards to proceed.

Setup Wizard step one - Configure the server - On the Identify Network Cards step, choose Continue anyway. Click Internet Connection to proceed.
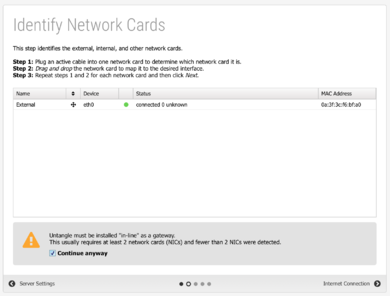
Setup Wizard step two - Identify network cards - On the Configure the Internet Connection step, confirm the Auto (DHCP) selection for the Configuration type and review the Status. Click Auto Upgrades to proceed.
Setup Wizard step three - Configure the Internet connection - On the Configure Automatic Upgrade Settings step, review the automatic upgrades and Cloud connection options. We recommend enabling both options. Click Finish to complete the wizard.
Setup Wizard step four - Configure automatic upgrade settings - If you selected Connect to Cloud in the final step of the setup wizard, follow the prompts to log in or set up your ETM Dashboard account to add the new appliance to your organization.
| To simplify the VPC deployment, NG Firewall for AWS requires only a single network interface. The internal network interfaces associate to each VPN tunnel or connection. |
Internet Hostname
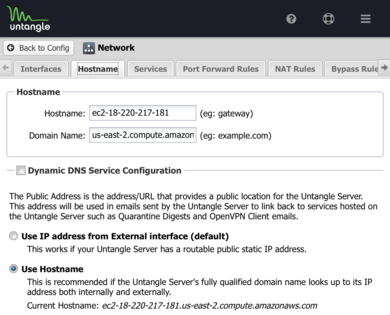
Components such as location services, notifications, and VPN profiles require knowledge of the Internet routable IP address that associates to the external interface of your instance. In AWS, instances use privately routable IP addresses and do not attach directly to the Internet. Therefore you must configure the NG Firewall with an Internet hostname that resolves to your Internet routable IP address or Elastic IP.
- From the NG Firewall web administration navigate to Config → Network.
- In the Hostname field, set the unqualified part of your Public DNS.
- In the Domain Name field, set the qualified part of your Public DNS.
- Select the Use Hostname option.
| You can set the Internet hostname using your own domain name. In this case configure your DNS with an Address Record (A) type that points to the Elastic IP address of your instance. |
VPN Server
After you complete the setup wizard you can begin the VPN configuration of NG Firewall for AWS. The VPN server enables remote hosts and networks to create a secure tunnel that routes traffic through the NG Firewall to access the Internet.
- From the NG Firewall web administration navigate to Apps → OpenVPN.
- In the Status tab, toggle OpenVPN is enabled.
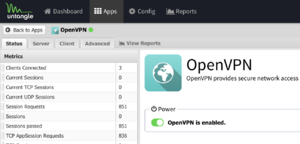
OpenVPN status view - In the Server tab, check Server Enabled.
- In the Server tab → Remote Clients tab, click Add to create a new profile.
- Assign the parameter of the profile. See OpenVPN for additional information.
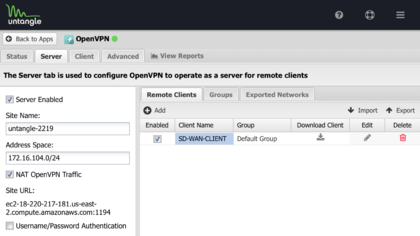
OpenVPN remote clients view
| For VPN tunnels with other vendors that do not support OpenVPN, use IPsec. See IPsec VPN for additional information and configuration details. |
Next Steps
After performing the initial configuration you are ready to fine tune your policies and set up VPN tunnels at remote sites. Here are some related topics to get your started: